1099 vs. W2 Employee
1099 workers are self-employed independent contractors. They receive pay in accord with the terms of their contract and get a 1099 form to report income on their tax return. In contrast, a W2 employee is entitled to a regular wage and employee benefits such as sick leave. The employer withholds income taxes from the employee’s paycheck and has a significant degree of control over the employee’s work.
Managing human resources is one of the most challenging aspects of running a small business. Without a dedicated HR team, it falls to you to handle onboarding, payroll administration, employee relationships, and other vital HR tasks. In addition to the time cost of these responsibilities, you also need to account for the monetary costs of staffing—which, depending on your industry, can eat up between 40% and 80% of your company’s budget!
Given this expense, many small business owners consider whether to hire a 1099 vs. W2 employee for certain positions. Hiring 1099 workers—or independent contractors as they are more commonly known—can help you cut back on costs and legal responsibilities.
There are some major differences between these two types of workers, and classifying them properly with the IRS is very important. Otherwise, you could face penalties from the IRS, or even a lawsuit against your business. For this reason, we recommend getting the assistance of an employment attorney when classifying your workers.
Aside from the legal issues, though, there are advantages and disadvantages both to hiring employees and independent contractors, and you want to make the right choice. Here, we’ll give you the lay of the land, including the characteristics of 1099 vs. W2 employees, when to hire which, and specific examples that you can apply to your small business.
1099 Worker vs. W2 Employee: What’s the Difference?
Let’s start by taking a look at the differences between a 1099 vs. W2 employee. Both are named after their respective tax forms: Companies provide a Form 1099-MISC to independent contractors that they work with, and employers file Form W2 on behalf of their employees.
Although both independent contractors and employees provide vital services to the small businesses they work for, there are several important differences between the two. Understanding these differences is vital—if an employee is misclassified as an independent contractor, you could be subject to costly fines and legal fees. And W2 workers who are misclassified as independent contractors can sue your business for benefits they were denied, such as health insurance, overtime pay, and the minimum wage.
To cut down on the confusion, we’ll go through the key identifiers for both types of workers, and how you can distinguish between the two.
What Is a 1099 Worker?
A 1099 worker—or independent contractor—generally provides specific services, as defined by a written contract. Some 1099 workers only work on one project at a time, but many serve multiple clients, providing a service within their expertise. Independent contractors, such as freelancers and consultants, are self-employed, so they’re business owners themselves.
Most of the time, businesses hire W2 employees with the intention of working with them for an undetermined length of time. On the other hand, businesses engage independent contractors for a defined period of time, per the conditions outlined in the contract. But that engagement may be renewed as many times as both the 1099 worker and the business owner find to be mutually beneficial.
No matter the length of their term, independent contractors define for themselves how and where they work, and what tools and methods they use to complete the work you hired them for. 1099 workers can also choose to hire their own workers to help them deliver the product or service that you hired them to provide. In other words, independent contractors assume the risk for their own profit or loss when they carry out their job.
Since your level of oversight over independent contractors is relatively low, your level of financial and legal responsibility is low, as well. 1099 workers pay both employee and employer self-employment taxes—so, if you choose to hire an independent contractor, your business doesn’t need to pay payroll taxes. And, as their own business owners, 1099 workers aren’t eligible for the benefits you might offer your W2 employees, such as health insurance, paid time off, and overtime.
What Is a W2 Employee?
A W2 employee is what we normally think of as a typical, salaried employee. Unlike independent contractors, W2 workers are not their own business owners. They work for your company, participate in employee benefit programs, and work according to your business’s needs and schedule. Unless there’s a compelling, clear reason to classify a worker as an independent contractor, the default classification is employee.
By law, employees are guaranteed at least minimum wage (set by both federal and state laws) for the time they’ve worked on a regular and ongoing basis. Companies withhold their W2 workers’ Social Security and Medicare taxes, and pay employer payroll taxes. In most cases, a company can let an employee go for poor performance or any other valid, non-discriminatory reason. An independent contractor, on the other hand, works and receives pay according to the terms of a signed contract between the parties. They also pay their own taxes.
Employers provide all the necessary tools and supplies for W2 employees. Independent contractors, on the other hand, must provide their own. In addition, employees are typically reimbursed for business expenses they incur over the course of their employment. This is typically not the case for independent contractors, unless specifically outlined in their contract.
Benefits like health insurance, retirement contributions, and flexible spending accounts are available to all qualifying employees in a business. As we mentioned earlier, benefits aren’t available to independent contractors doing work for a business.
How to Determine Whether Your Employees Are 1099 vs. W2 Employees
We noted the importance of correctly classifying your employees as 1099 or W2 workers with the IRS. Often, cost and ease are the key determining factors a business owner considers before choosing whether to engage a contractor or hire an employee. To be fair, it’s much easier to pay a contractor than it is to administer payroll and handle other HR functions required of a business with employees.
But any cost and time savings will quickly disappear if the IRS or Department of Labor audit you and find that you’ve misclassified workers. The penalties are pretty hefty. The IRS could levy back taxes and penalties of more than 40% of the contractor’s pay. And the DOL could require you to pay wages going back three years.
Admittedly, the line between 1099 and W2 workers can become a little blurry—but the IRS provides some guidance about how to correctly classify your workers. The IRS considers three major categories in determining whether workers are employees or independent contractors:
- Behavioral – Can your business control what, where, how, and when the worker carries out their job?
- Financial – Who controls the economic aspects of the worker’s job? What’s the method of payment (e.g. a regular salary or a flat fee)?
- Type of relationship – Do you provide this worker with employee benefits? What are the length and terms of this relationship, as outlined in a contract, employment agreement, other documentation?
According to the IRS, what the employee classification process really boils down to is the level of control a business has over the worker. If the company controls most of the person’s work, then the worker is most likely a W2 employee. If the person has a good degree of independence, they’re most likely a 1099 independent contractor.
If you’re unsure whether a member of your staff is a 1099 vs. W2 employee, after weighing the three factors above, you can file Form SS-8 with the IRS. In that case, the IRS will make a determination for you about how you should classify your employees. The IRS can take up to six months to decide, but this is helpful if you tend to hire for the same types of roles at your company.

1099 vs. W2 Employee: Which Is Better for Your Business?
Now that we know the difference between an independent contractor and a W2 employee, it’s time to answer the question you’ve probably been asking yourself: “Which type of worker is better for my business?”
Many small business owners choose to work with independent contractors because of the perceived cost savings. Employment taxes, workers compensation insurance, overhead costs like office space and break-room supplies—they’re all necessary expenses when you hire W2 employees, and they can quickly erode a business’s bottom line. In addition to the costs, though, you’ll also need to weigh the other pros and cons of each option.
Advantages of 1099 Independent Contractors
- Bring specialized expertise – One of the biggest benefits of working with an independent contractor is that most focus on one thing and do it really well. For example, if you have a project requiring very specific design or tech expertise, then you most likely will be able to find an independent contractor who has built a business around this.
- Offer greater flexibility – As opposed to a regular employee, who stays with your company for the long haul, you can hire an independent contractor just for a project or two or as your budget allows. This gives you more flexibility when company priorities and resources shift.
- Less legal risk to your business – Independent contractors are not eligible for workers compensation coverage, can’t bring most types of wrongful termination claims, and usually carry their own professional insurance. That lowers your company’s legal exposure.
- Lowers business costs – Cost is certainly an important factor, and you can save money by utilizing a 1099 vs. W2 employee. You don’t have to provide a minimum wage, overtime, or benefits to independent contractors. Since you don’t have to withhold income taxes or pay payroll taxes, there’s also less of a paperwork burden on your company when you hire independent contractors.
Advantages of W2 Employees
- Committed to your company – Treat them right, and employees can bring big dividends for your business. They will feel loyal to your company and go the extra mile by doing good work. There are many excellent independent contractors as well, but often, you’re just one client among many.
- Offer more continuity – Employees are with your business for the long haul, and they can lend a hand no matter what your business needs at a specific time. For example, if you need someone to shift focus or contribute to a project on short notice, you can rely on your employees to help out. Independent contractors, however, usually have a specific area of focus.
- Free up the business owner’s time – Being a small business owner requires you to wear dozens of hats, and sometimes you might feel like you can’t get a break. Having employees allows you to delegate specific tasks for the long term, so they’re off your plate for good. That frees you to focus on higher-level business decisions.
- Need to train them just once – Employees need to receive training as part of their initial onboarding process. And although they should receive periodic training after that, they’ll naturally be aware of company policies and expectations. Independent contractors aren’t part of your onsite team, so you can’t always expect them to deliver work that meets your standards.
Ultimately, you can’t really say that a 1099 is better or worse than a W2 employee across the board. The choice between a 1099 vs. W2 employee comes down to your business’s budget, the type of work, and the amount of control you’d like over the process and final product. Although their services might be more expensive than those of an employee, an independent contractor’s expertise can often yield a higher-quality product. But when you work with an independent contractor, you relinquish control over how, when, and where they do their work. For some small business owners, that can be a no-go. And many small businesses think of their companies as one big family, and employees fit that model better than independent contractors.
There’s a lot to consider when you’re choosing between hiring 1099 vs. W2 employees. To help you out, consult the following table. This highlights some specific scenarios where you might choose an independent contractor over an employee, or vice versa:
Examples: When to Choose a 1099 vs. W2 Employee
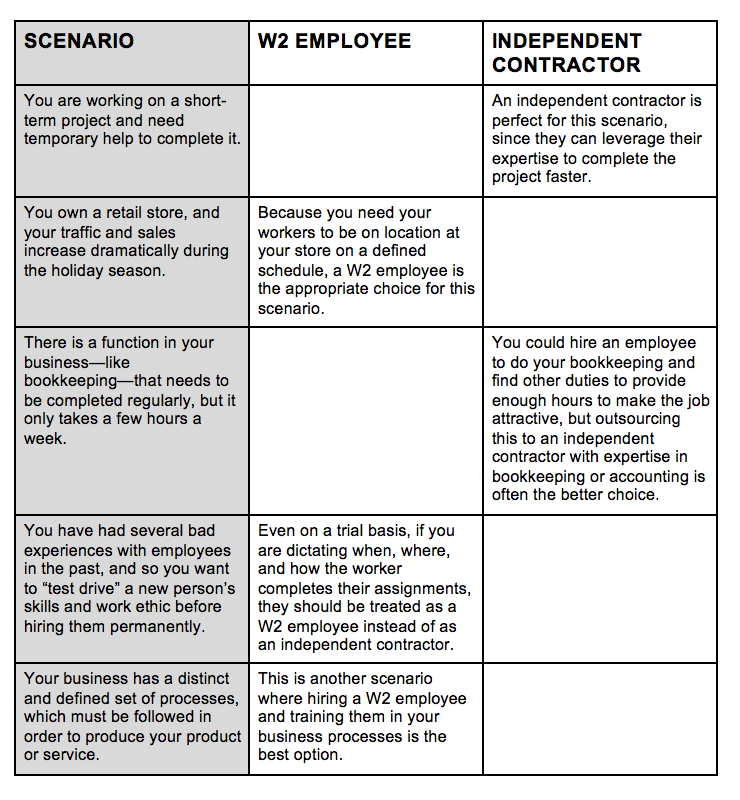
As you can see, sometimes it makes more sense to engage the services of an independent contractor than it does to hire an employee. At other times, though, you’ll need to hire an employee to get the job done. If you’re still not sure which type of worker you should hire, there might be some alternative solutions at your disposal.
Not Ready to Hire 1099 or W2 Employees? Consider These Alternative Staffing Options
If you’re not ready to decide whether to hire a 1099 or a W2 employee, there are two alternatives that combine some elements of both—temp agencies and professional employer organizations. Both of these options give you access to a pool of qualified workers, but you won’t need to worry about classifying them as either 1099s or W2 employees.
When and Why to Hire Through a Temporary Agency
Seasonal businesses or businesses that want to “test drive” an employee before hiring them on a full-time basis might consider using the services of a temp agency.
When you contract with a temp agency, the agency takes care of recruiting, interviews, background checks, and timely payroll processing and tax payments. The temp agency also invoices your business for the employee’s wages and taxes, and a service charge for the administrative services the agency provides. This invoice is recorded as a simple business expense on your books, and you don’t have to worry about tax filings, workers compensation insurance, or other human resource issues. On paper, the official employer of the worker is the temp agency, not you (unless the position is a “direct hire“). However, you get to decide how long the worker will work at your company and specify their day-to-day tasks.
This option costs more than administering your own seasonal or temp-to-hire workforce, but the time savings could well offset the additional cost. Just don’t create a false sense of security for yourself. Even though the temp isn’t your direct employee, this doesn’t mean you can’t be held legally responsible if something goes wrong, such as a workplace accident. And worker quality might be a problem when temp agencies act as the middle man.
The Benefits of Staffing Your Business Through a PEO
Temp agencies are a temporary solution to short-term employment challenges. There is, however, a longer term solution called a professional employer organization—or PEO. PEOs let businesses outsource HR tasks like payroll, workers compensation, and benefits, while retaining control of the employee’s day-to-day responsibilities.
In addition to relieving small business owners of the administrative burdens associated with managing employees, PEOs can also leverage the number of employees they manage across companies to get better benefit options than small businesses alone can negotiate. As is the case with temp agencies, PEOs charge a fee for their services, but the benefits may outweigh the costs.
Your company and the PEO both act as joint co-employers of the worker. You manage the worker on a daily basis, but the PEO is the worker’s go-to for anything administrative or HR-related. The sharing of responsibilities will be outlined in a written PEO arrangement.
Whether you choose to use a temporary agency or engage the services of a PEO, it’s imperative that you do your due diligence. Ask the temporary agency or PEO for references, and follow up with other small business owners who have used their services.
And, as is always the case when you enter into a business contract, you should also hire an attorney to review any agreement with a temp agency or PEO before you sign. This ensures that you’re not inadvertently taking on liabilities that you believe the temp agency or PEO should be covering.

1099 vs. W2 Employee: A Complex Consideration
One of the most important tasks you’ll undertake as a small business owner is staffing your organization with the best possible workers. The question, though, is which kind of worker you should hire. Here’s a quick refresher.
- 1099 workers, or independent contractors, are self-employed. You can hire 1099 workers for specific projects, but you can’t control when or how they complete their jobs. You’re not responsible for covering their Medicare and Social Security taxes, and you won’t provide them with the same benefits as you would for a W2 worker. This may be the less expensive option.
- W2 workers, on the other hand, require a regular salary, certain benefits, and more intensive management. The financial costs of hiring W2 employees may be higher than 1099 workers. But you might prefer to have a steady team of employees on hand, whom you’ve trained and can manage according to your standards.
In all, you’ll need to carefully weigh a few considerations before making your decision, including the type of work you need completed, how quickly you need that job done, whether the job is a one-time or regular commitment, and the costs attendant to hiring 1099 vs. W2 workers.
The best practice is to consult an employment attorney and tax professional before making your final decision about how to consult your business’s workforce.
The post 1099 vs. W2 Employee: Which Is Better for Your Business? appeared first on Fundera Ledger.
from Fundera Ledger https://www.fundera.com/blog/1099-vs-w2-employee/
No comments:
Post a Comment